Life on Mars? The Discovery That Could Change Everything
NASA’s Perseverance rover has once again reignited one of humanity’s most fascinating questions: Did life on Mars ever exist?
The latest analysis of Martian rocks in the Bright Angel region of Jezero Crater is not only a breakthrough in planetary geology but also a potential window into the ancient microbes that may have once thrived on the Red Planet.
The Rock That Keeps Scientists Awake
Geologist Michael Tice from Texas A&M University admits he had never lost sleep over a rock—until now.
A sample collected from a formation called Cheyava Falls shows surprising chemistry: redox reactions (oxidation-reduction) very similar to those driven by microbial activity on Earth.
In other words, the rock may contain fossil-like traces of ancient microbial life on Mars, dating back about 3.5 billion years, when the planet was wetter and much more habitable than today.
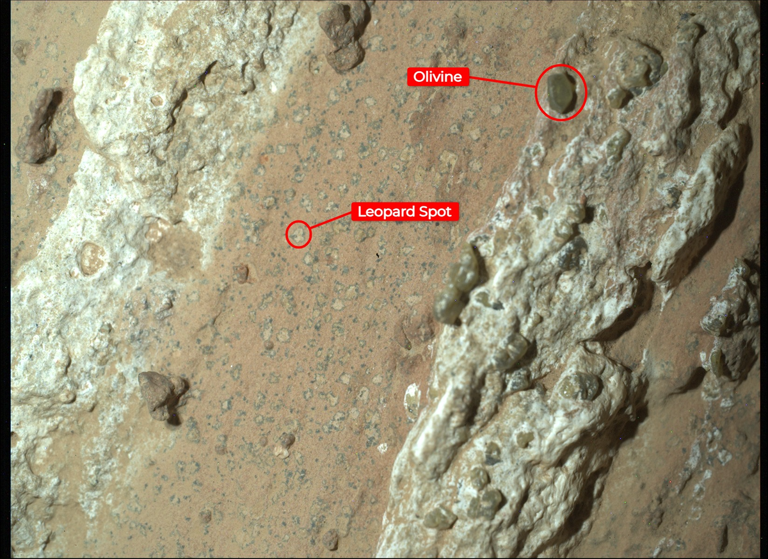

The “Poppy Seeds” and “Leopard Spots”
The analyzed rocks display tiny structures nicknamed “poppy seeds” and “leopard spots,” rich in minerals such as vivianite and greigite.
On Earth, these formations are often linked to biological processes: microbes consume organic matter to generate energy, leaving these minerals as byproducts.
If the same process occurred on Mars, it would mean that two different planets hosted forms of life capable of extracting energy in identical ways. This would radically change our understanding of the universal evolution of life.
Not Just Biology: Geological Alternatives
Of course, scientists remain cautious. Similar processes can occur without life, for example in volcanic environments at high temperatures. However, in the case of Cheyava Falls, there is no evidence of extreme heating—making the biological hypothesis one of the most convincing.
To reach a definitive answer, scientists would need to return the samples to Earth, where advanced laboratories could analyze them in greater detail. For this reason, both NASA and the ESA are planning Mars Sample Return missions between 2028 and 2030.
Mars and the Future of Exploration
Whether these are fossilized microbes or simple chemical curiosities, the discovery pushes humanity further toward the exploration of Mars. Every rock Perseverance examines tells not only of the past but also of our possible future colonization of the Red Planet.
Science Meets Curiosity: 3 Amazon Picks for Space Enthusiasts
If this discovery has sparked your curiosity about space exploration, here are three fascinating tools and books you can enjoy from home:
-
🔭 Celestron AstroMaster 70AZ Telescope – perfect for observing the Moon, planets, and imagining yourself peering into Jezero Crater. Check it out on Amazon
-
📚 Astrobiology: A Very Short Introduction – a brilliant book explaining how scientists search for life beyond Earth. Available here
-
🚀 LEGO NASA Mars Rover Perseverance – build your own model of the rover that made this historic discovery. See it on Amazon
A Final Thought
Perhaps we will never know for certain whether microbial life on Mars once colonized its ancient waters. But each new finding, like the chemical fingerprints at Cheyava Falls, brings us closer to an astonishing truth: life may not be a cosmic exception, but a rule.
If that’s the case, gazing at Mars may actually mean looking into a mirror of our own most distant past.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links to Amazon.com. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. This comes at no additional cost to you and helps support the maintenance of this website.







Leave a Comment