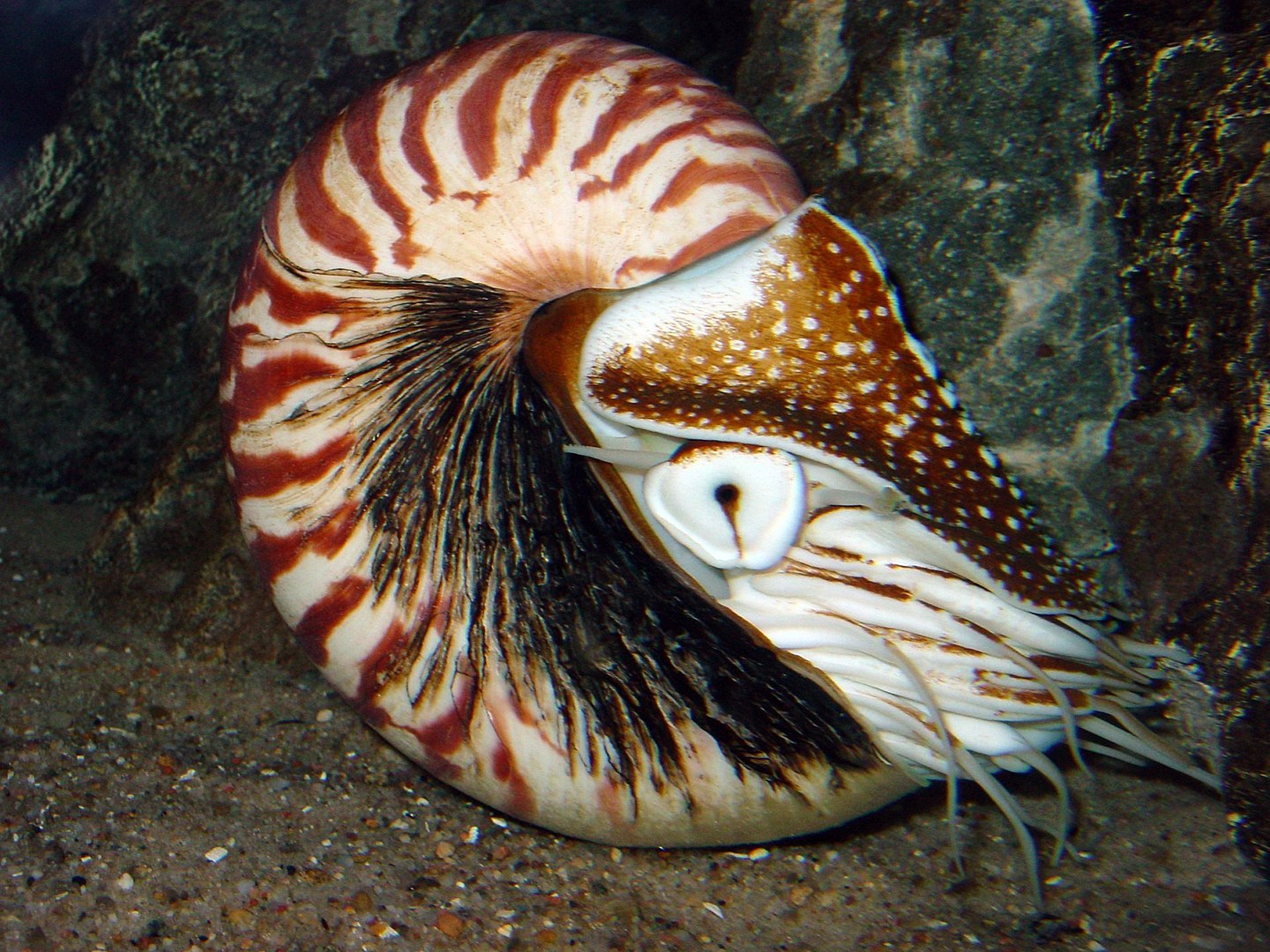
Deep in the world's oceans, hidden in the twilight zones where few creatures dare to venture, survives one of nature's most extraordinary relics: the Nautilus. This ancient marine being, with its mesmerizing spiral shell, has remained virtually unchanged for millions of years, making it one of the most remarkable living fossils known to science. A silent witness to Earth's evolutionary saga, the Nautilus continues to navigate the depths, defying extinction where many of its relatives have perished.
A Traveler from the Past
The Nautilus belongs to the class of cephalopods, the same group as octopuses and squid, but unlike them, it has retained its characteristic external shell. The first forms of Nautiloids appeared around 500 million years ago, during the Cambrian period, and reached their evolutionary peak in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras, when they dominated the seas alongside the ammonites. However, while the ammonites went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous, the Nautilus managed to survive to this day, remaining virtually unchanged for over 150 million years.
Unique Anatomy and Adaptations
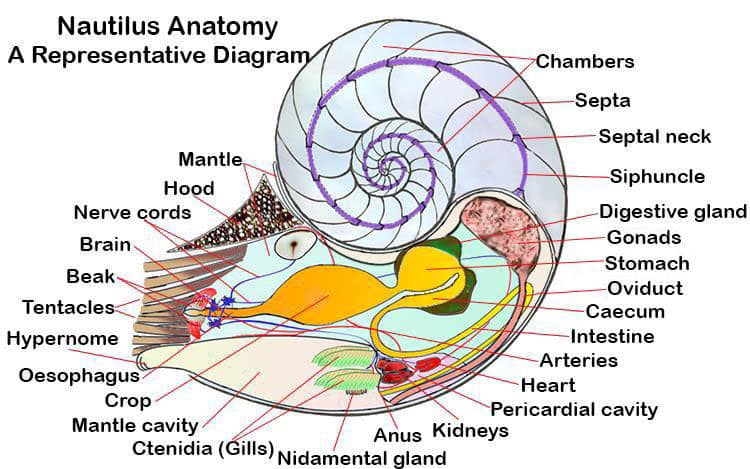
The Nautilus is easily recognizable due to its iconic spiral shell, divided into separate chambers. The animal lives in the last chamber and utilizes a sophisticated buoyancy control system based on the principle of osmotic pressure: by regulating the amount of gas and liquid in the internal chambers, it can precisely control its depth in the water.
Unlike octopuses and cuttlefish, the Nautilus has numerous tentacles without suckers (up to 90 tentacles), which it uses to capture prey and perceive its surroundings. Its vision is less developed than that of its modern relatives, but it compensates with an acute sense of smell, helping it detect food and predators.
Internal anatomy of Nautilus pompilius - Wikipedia
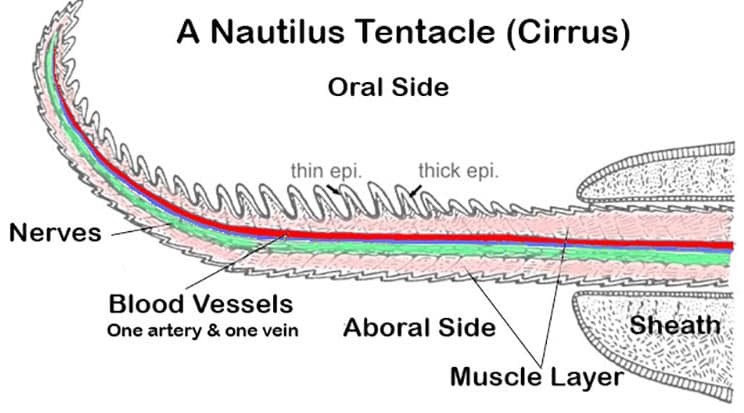
Source - Earthlife.net
Habitat and Behavior
The Nautilus inhabits the deep waters of the Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean, between 100 and 700 meters in depth, preferring rocky seabeds and coral reefs. It is an opportunistic predator, feeding on small crustaceans, dead fish, and other benthic organisms. At night, it ascends to shallower waters to search for food, returning to greater depths during the day, a behavior known as vertical migration.
A Symbol of Evolutionary Resilience
What makes the Nautilus a living fossil is its extraordinary evolutionary stability. Its main characteristics have remained unchanged for millions of years, suggesting an exceptionally effective adaptation to its environment. However, this same specialization makes it particularly vulnerable to climate change and human activity. Overfishing for its shell, highly prized in the trade of souvenirs and decorative objects, has significantly reduced Nautilus populations, leading some countries and organizations to advocate for its protection.
The Future of the Nautilus: Evolution or Extinction?
The Nautilus is at a crossroads between survival and decline. On one hand, its long history suggests an extraordinary ability to adapt, but on the other, modern environmental pressures could threaten its existence. Some biologists hypothesize that if it survives long enough, it may develop adaptations to cope with the increasing acidification of the oceans or even modify its feeding and reproductive behavior to adapt to a changing world.
Legends and Symbolism of the Nautilus
The Nautilus has fascinated humankind since ancient times, often associated with the golden ratio due to its spiral shell, a symbol of harmony and infinite growth. In literature, the famous submarine of Captain Nemo, in the novel Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea by Jules Verne, takes its name from this creature, evoking its mystery and resilience in the ocean depths.
The Nautilus is a reminder of the fragility of life on Earth. Protecting this species means preserving a piece of living history, a direct link to the remote past of our planet. Whether it will continue to endure or disappear like the ammonites before it depends not only on nature but also on human choices regarding the marine ecosystem.







Leave a Comment